Mapping railway processes with SAP S/4HANA transportation management and leogistics rail
Rail transport still serves as the backbone of an efficient industry today. It is therefore worthwhile to take a closer look at the various possibilities of digitalization for this mode of transport. In our blog series, we deal in detail with SAP S/4HANA Transportation Management in the field of rail-bound transports. After looking at the basics of rail transport in the system, after reviewing the planning of single wagon, manifest and block train transports, the transport execution and the invoicing of transport services, we now focus on loading point and shunting processes and devote ourselves to the reporting of rail services.
Shunting operations in stations
The system functions considered in our blog series relate primarily to transport processes on railway lines. Train dismantling, loading point operation and train formation have not been considered so far – for a simple reason: SAP S/4HANA TM does not map these shunting processes systematically. To close this gap, we have developed leogistics d.s.c. in the form of leogistics Rail!
What is leogistics rail?
leogistics Rail is a system to support the planning and handling of operative railway processes in sites and plants (local facilities). If configured accordingly, one is informed about all incoming, yard-internal and outgoing movements of railway wagons for one plant or even across several plants, e.g. in inter-plant traffic.
All wagons on site are displayed at their respective location (track and position in the track) and their current (load-related and technical) characteristics. In addition, leogistics Rail is used to plan loading point driven shunting movements as well as incoming and outgoing train treatment of trains.
Ideally, leogistics Rail is connected to the following systems via interfaces:
- SAP TM: Transportation planning system, as upstream integrated planning tool
- Railway Undertaking (RU): train reservation, train consists, train status report
- Loading points:
- to assign requirements to (empty) wagons and to map the loading and unloading process
- for visualization of current track occupations
- Track scales
- a system for automatic processing of incoming or outgoing wagons at the site (e.g. RailWatch)
The interaction of SAP TM and leogistics rail
The process
Based on the transports (train runs) planned in SAP TM, leogistics Rail automatically creates the following information necessary for the operative handling of the associated rail processes:
- Planned incoming trains
- Planned outgoing trains
- Demand for wagons for the specific loading points at a specific time (according to loading planning from TM)
The requirements can be loaded wagons with a certain load, but also empty wagons with a certain load and/or loading point specific characteristics.
With the transmitted information, leogistics Rail starts planning the necessary wagon movements depending on the following factors:
- necessary inbound train checks
- Current stock situation (track capacity)
- desired operating time of the charging points
- any scheduled shunting movements through the plant
- the availability and utilization of shunting vehicles and the corresponding personnel
- the availability of wagons (differentiated here according to the aspects “not available, as not yet in the factory” or “not usable due to audit or damage”)
- proposed outbound train formations
After successful planning, the locomotive shunting teams are commissioned via specific shunting orders, which are then implemented by them. The system supports this process by connecting a mobile shunting app, which can be used to record all movements (start, destination, any unscheduled intermediate stops) by the shunting team via smartphone or tablet.
The information on wagons and loads planned for specific outbound trains also enables the trains to be planned and formed in advance in line with demand and time.
After the departure of an outgoing train, all data relevant to invoicing for the corresponding wagons and loads, such as
- movement information
- shunting to/from loading points
- start date and time
- rail car condition (damage condition, revision condition)
and can be transferred to the TM for accounting or reporting purposes.
The wagon management
We have already described the SAP TM Railcar Resource in detail in the first part of the blog series.
leogistics RAIL offers the possibility of extending SAP TM Wagon Management with additional genus/type or even wagon-specific master data and functions, which are necessary for operative processing, among other things.
In combination with leogistics Rail master data management, it is possible to set up a comprehensive wagon database of rented empty wagons as well as the in-house wagon fleet.
Part of the solution is a comprehensive European collection of wagon types. Derived from the wagon number (which is transmitted to the system, e.g. by means of pre-reporting), the basic properties such as length over buffer, tare weight and capacity are preassigned as far as reasonable and possible.
The basic wagon master record created with this information can be supplemented with further details such as brake data, boiler data or specific grids for load limits or revisions, manually and via interface, e.g. by a wagon adjuster.
Revision data are of course included in the calculation of available (empty) wagons at the locations. In addition, the wagon scheduler is informed of upcoming revision dates and the rail cars are flagged accordingly in the system.
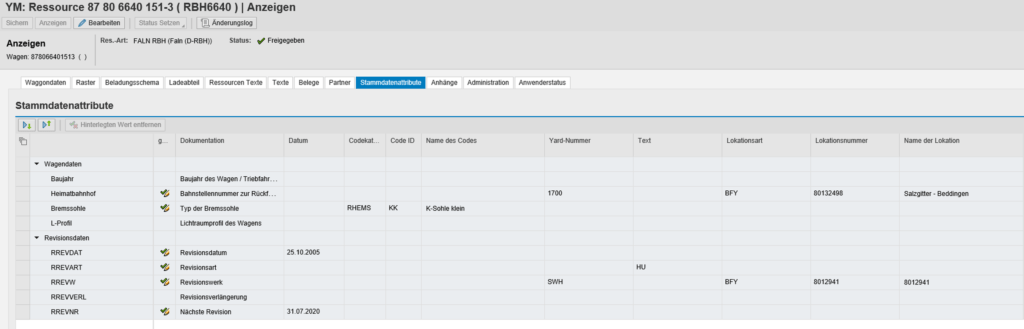
Photos can be uploaded directly to the railcar master record. With integration to camera sensors at the location, daily updated photographs of the individual railcar can also be stored in the system.
Recording damage
For the documentation of wagon damage, users have access to a mobile application with damage codes according to the GCU (General Contract of Use for Wagons) and an integrated photo function. This not only enables complete logging in the system, but also serves to automatically propose follow-up actions and processes, e.g. the transfer of the damaged wagon to the workshop.
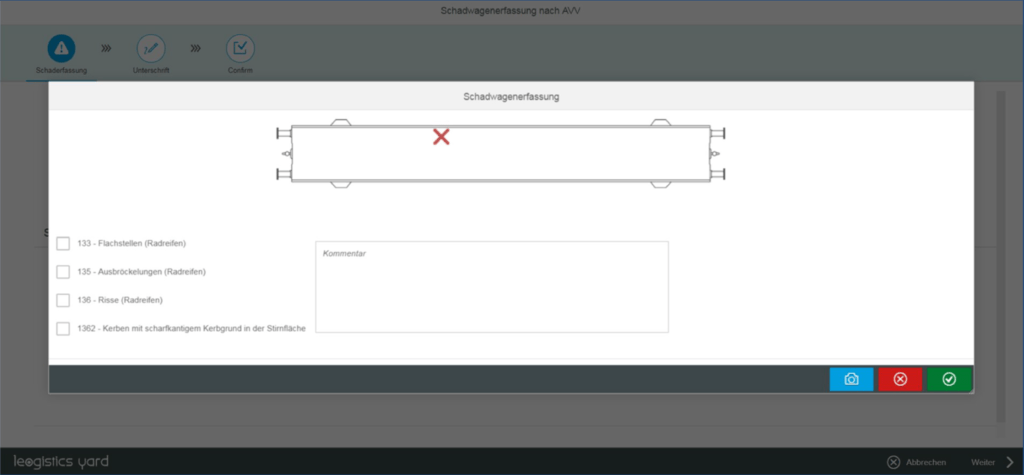
Alternatively, damage is also transmitted by the adjuster via interface and stored in the system. Downtimes due to damage are included in the wagon availability at the locations – analogous to the inspection times.
Where are my cars?
The current position of the individual wagon or train is relevant for the transport and wagon deployment planner both within a railway station and on an open route.
The system offers a schematic or visualized track diagram overview for a yard. Based on the shunting movements, the current track and position in the wagon train is documented and displayed for each wagon.
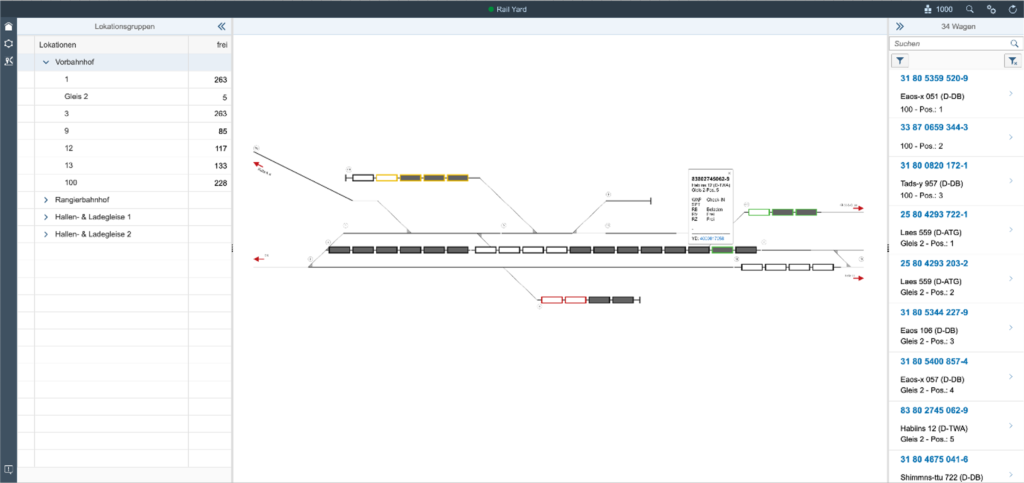
There are two types of tracking and tracing on the open track:
- passive position determination through feedback from the RU (e.g. message IFTSTA from DB Cargo)
- active position determination by GPS terminals on the individual wagon; in practice, this can be realized above all with the company’s own fleet of wagons
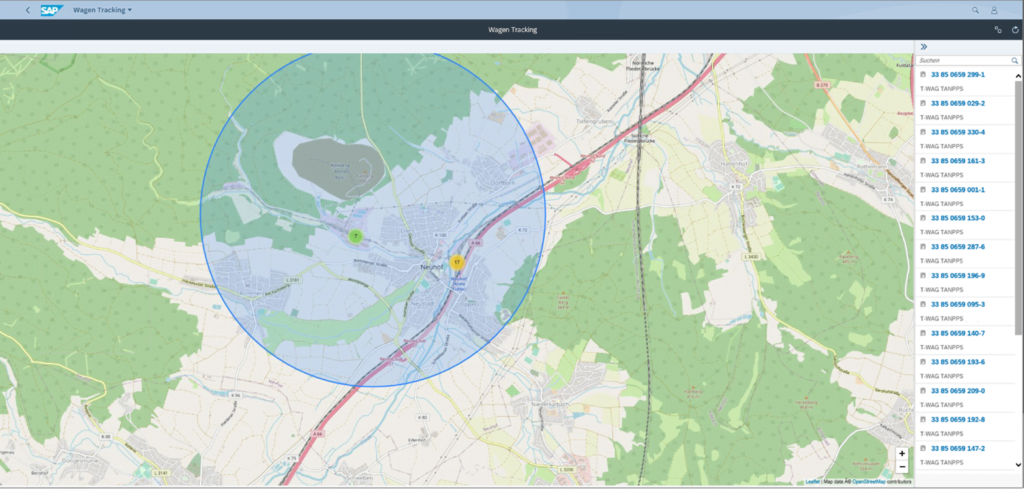
Location data of individual wagons can be bundled to form a train run. The system actively reports delays and disturbances and proactively suggests possible follow-up processes (e.g. using an alternative train path).
The system is also able to detect the uncoupling of cars en route (in the event of damage or a hot box) or the erroneous placing of empty wagons on external, unplanned railway stations. Here, too, the system can alert the wagon scheduler based on the defined business rules in order to avoid high downtime costs.
Evaluation and analysis of all railway-specific services
With this multitude of wagon and train services, it is important to keep track of the numerous individual rail freight orders. This raises numerous questions with regard to the rail transport companies used:
- Quantity of freight orders per period
- Quantity of on-time freight orders per period
- Quantity of tonnages transported per period
- Evaluation of available wagons per period
SAP S/4HANA Transportation Management provides both table-based and graphical reporting for this purpose.
Table-based reporting
Within SAP TM it is possible to work with operative data in numerous places using worklists (Personal Object Worklists, POWL). Within these worklists you can define your own queries, which are either user-specific or role-specific. Worklists can be sorted, aggregated and exported to Excel. Using worklists, it is also possible to perform activities for several data records simultaneously.
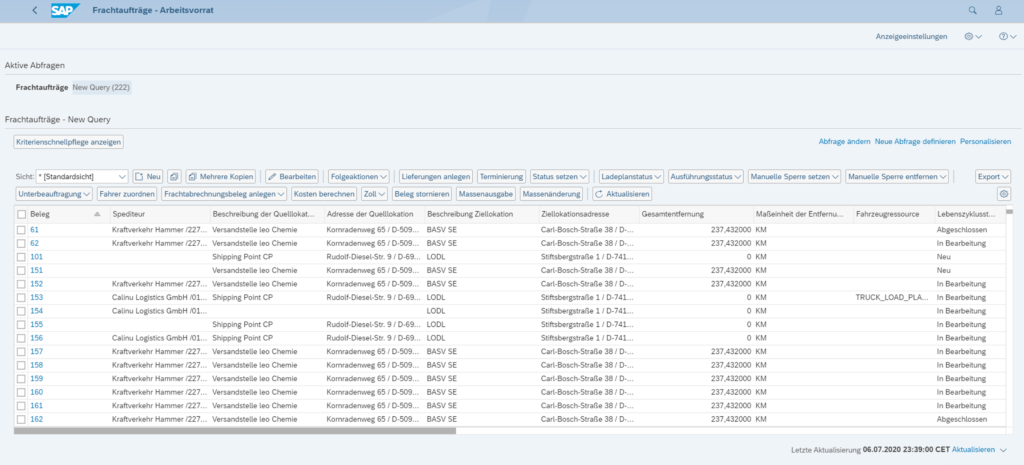
Graphic reporting
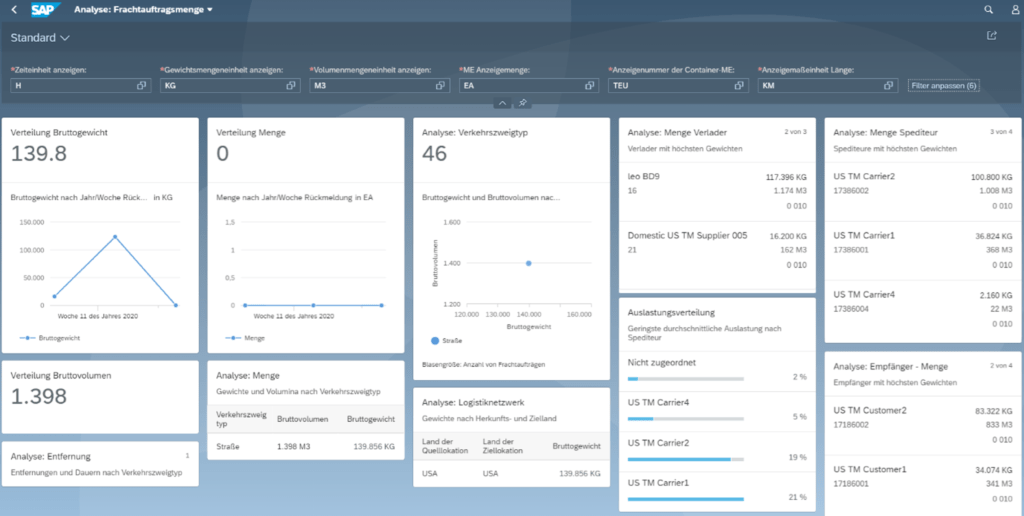
SAP S/4HANA 1709 also enables graphical reporting for operative periods in so-called embedded analytics. This reporting solution enables operative real-time analyses of the data in the HANA database for the Transportation Management division without a separate reporting system. Here, overview pages from different areas of transportation management are provided in the form of Fiori UI applications, which include different KPIs and can be adapted. Whether for the overview of contingents, transport costs or freight order quantities.
Our concluding remarks
In the past weeks we have intensively dealt with SAP S/4HANA TM and the possibility to map railway processes in it. SAP TM as a toolbox offers many helpful tools that can be used out of the box, such as resources, timetables and receipts. The possibilities that SAP TM offers for rail processes are also manifold in the area of shipment cost accounting and settlement.
In this article we also briefly discussed the operational handling of railway processes, and in particular plant railway processes. Here, if you want to move completely within the SAP standard, your hands are tied. For the planning and execution of shunting orders, for mapping the current operational situation on the site and in reporting, leogistics RAIL offers the possibility of closing gaps in the IT-side process mapping. In individual cases, further process steps can also be detailed, such as through the use of a detailed wagon database or improved connectivity.
This is also the conclusion we come to when we take a detailed look at the individual customer challenges we face in our projects. We will be happy to report more about this soon!
Have we aroused your interest? Then get in touch with us!
If you have any questions about this or other topics in the blog, please contact blog@leogistics.com.
Marco Mohr
Christian Sachse
Matthias Platzer
Consultants SAP Logistics




