Your approach to smart yard management
Efficiency and process reliability are certainly the strongest arguments for the introduction of smart yard management. This usually involves transparency (Who is on the premises?), information (What is where on the premises?) and time (How long has someone or something been on the premises?). But what exactly makes site logistics and thus a yard management software smart? This is the question we are looking into today, and in doing so, we are giving an outlook on the possibilities of digitalization and automation in yard logistics.
What Is yard management?
Logistical processes outside of and on site have an enormous influence on the effectiveness and efficiency of the flow of goods. Yard Management is a software solution that harmonizes the flow of goods, means of transport and information. The overall goal is to make internal plant transports transparent and to plan and control them efficiently.
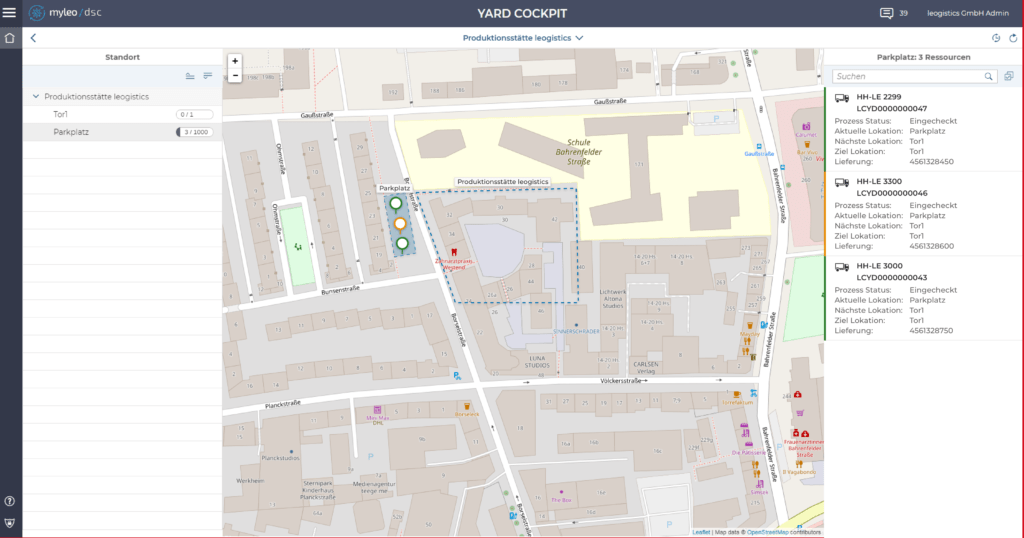
Classic component of yard management
| Logistics process management | Process administration and scheduling are the focus of yard management. It is essential to manage all logistic units (such as trucks, forklifts and goods) so that they are available at the right time and in the right place. |
| Administration | Administration Various overviews are available that reflect the current operating situation (who is when, where and why in the yard?). Dashboards display operational key figures as well as consolidated information in list form. |
| Gate Management | Gate Management To ensure safety, access to the site is generally restricted. Check-in and check-out processes are used to control incoming and outgoing transports, flows of goods and access of persons with the help of barriers and gatekeepers. |
| Appointment Scheduling | Often, exact control is only possible by reserving scarce resources. With dock/door appointment scheduling, you can regulate means of transport that can be handled at the same time. Means of transport that are not on time or that exceed the currently manageable volume are managed in parking and waiting areas. |
| Resource management | Resource management as a special form of yard management organizes and optimizes the efficient use of resources for the transport of load carriers (such as swap bodies, wagons and trailers) by equipment (such as forklift trucks, shunting locomotives) on the factory premises. |
| Integration / Interfaces | Yard management processes form the link between storage, transport and production processes and corresponding systems. Integration aspects and interface capability are therefore a fundamental basic function. |
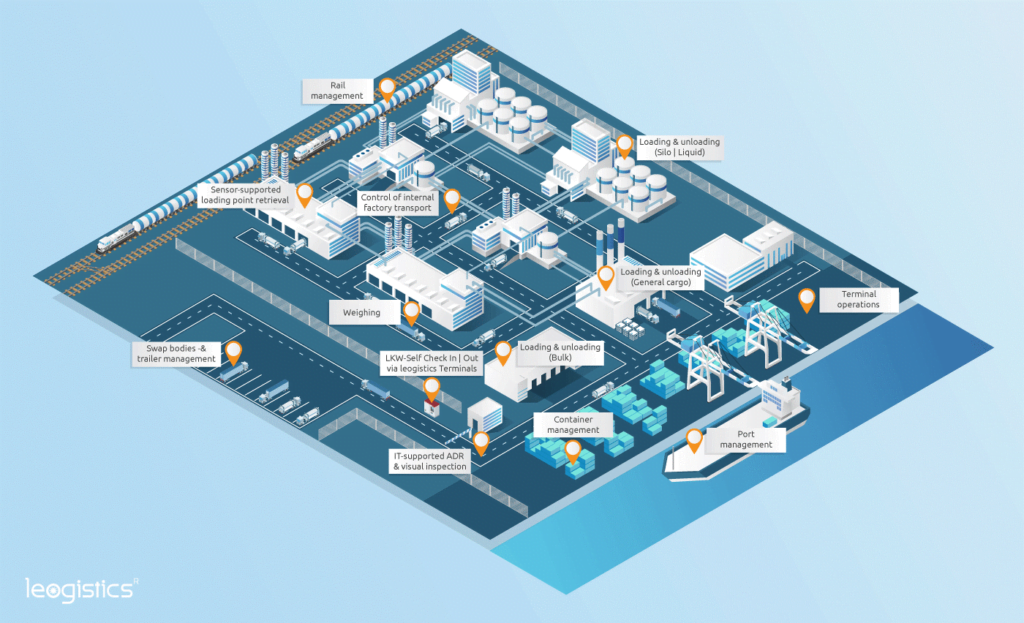
How's the yard smart?
A smart yard fulfils several objectives:
- Reduction of waiting times for all process participants (such as truck drivers and warehouse workers)
- Optimal utilization of the loading points
- Shortening of processing times.
To meet these objectives, it makes sense to examine your logistics processes from different angles:
Completely digitalized processes
Anyone who wants to rely on transparency and management by exception needs a meaningful picture of all processes on the plant premises at all times. To achieve this level of information, it is necessary to map processes digitally and to record the respective status in real time. Wherever today’s operations are carried out by radio or telephone, apps for communicating with drivers on work orders and task status can be helpful. Where previously information was passed on on paper or lists were ticked off, you can rely on electronic workflows and mobile applications.
The digitalization of the yard is completed by the use of sensor technology and IoT:
- You only load when the temperature in the staging area moves within a defined corridor? Then connect smart thermometers to the opening mechanism of doors. In a central control station, you can monitor the loading processes and temperatures.
- You would like to automate the Gate-In process for your own vehicles? Then use OCR cameras at the barrier and open automatically when truck license plates from your own fleet are recognized.
- You would like to have the factory transport run independently and without loss of time? Then rely on self-check-in terminals, calling up trucks with push notifications and directing traffic via navigation information boards.
Smarte management of containers and returnables
With real-time tracking and real-time visualization, you enable the control center to detect discrepancies even from a greater distance and to intervene in ongoing processes to correct them. What is the current gate allocation? How busy is the waiting area? Are there enough swap bodies in the yard? If you have equipped vehicles and containers with tracking units and track them on a map, you can identify problems early and avoid high search costs. Sensors installed on the ground for open storage or laser systems in silos record stock levels in real time and can optimize inventory management processes with automated incoming and outgoing postings.
Heat maps can help you identify inefficient processes or overloaded resources. Based on information from process and sensor technology, you can use information gathered from the execution to draw conclusions about the quality of planning.
Integration
Do you already include detailed information about deliveries and collections in your planning? And do you already know the details of the driver and the vehicle during the approach?
The higher the degree of integration with the other processes of the company and the supply chain, the more diverse the possibilities for using information. Collaboration along the supply chain allows you to use real-time information about trucks in the inbound for planning or to track the delivery until the proof of delivery.
Within your own IT infrastructure, the integration of yard management with your ERP can enable a detailed view of logistics costs.
Using AI
Especially in the cloud, the possible applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence are becoming increasingly diverse. For example, algorithms already support the planning and rescheduling of truck appointments. Systems thus learn and change routines, for example when prioritizing deliveries.
What does this mean for my industry?
Yard management must meet different requirements in different sectors and industries. This is mainly due to the corresponding logistics structures, product diversification but also to the physical conditions of a corresponding logistics location.
The consumer goods manufacturer
High throughput, frequently changing ramp contacts, pallet exchange and very close integration with warehouse logistics are the special features of the FMCG sector. By using time slot management and a tight dovetailing of warehouse and transport processes, the first smart yard targets can already be achieved. By means of time window planning, the warehouse is informed when which transport is due for loading. The warehouse can then transfer the corresponding gate planning to the yard.
The aim is to ensure that the right goods are available on the proper ramp at the correct time and that the warehouse and yard are informed in advance about the exact arrival of the truck. By means of telematics integration, retrieval orders can be initiated fully automatically. Entry, gate calls and driver communication can be supported by apps and sensor technology. If the processes are well coordinated, waiting times are extremely short or even non-existent. Loss of information due to language barriers can also be minimized by using multilingual apps.
The chemical park
Chemical logistics and the associated processes in the chemical park place special demands on the yard management. It is often necessary to be able to map different, multimodal transport chains in the yard, depending on the transported goods and customer region. These include classic truck transport for packaged goods, bulk transport for liquid goods by road or rail, handling of tank containers, container depot processes, inland waterway shipping and support for complete disposal processes.
Due to the hazardous nature of the goods to be loaded and transported, this aspect must of course also be taken into account in yard management – with special care and appropriate checks of the personnel and loading equipment.
The logistics provider
Logistics service providers or contract logistics providers must be able to serve a large number of different customers with individual requirements at their locations. In addition to system integration with the customer’s system (notifications) and corresponding freight carriers for delivery and pick-up, special processes such as value-added services or inspections must also be mapped in the yard.
This is clearly illustrated by the example of automotive compounds (finished vehicle yards): In addition to value-added services such as mirror mounting or battery replacement and installation, damage tests must be carried out and digitally processed. Where is the potential for smart processing?
- Work orders can be processed using mobile apps and digitally documented.
- Location data can be used to record an exact picture of the time and place of services. Smart camera recognition systems (OCR) can already detect patterns or damage when the vehicles are accepted.
Processes can also be made smarter in the general contract logistics sector. By simplifying master data and mapping yard management and time slot management processes in the cloud, locations and services can be switched live within a few hours. In addition to smart use, there is also a smart cost advantage for a highly flexible business model.
Cost-saving potentials through efficient plant logistics
Regardless of the degree of digitalization and automation, costs can be saved by efficient process design in the yard. Demurrage charges can be reduced or even avoided if the loading and unloading processes are precisely planned and the actual resources available are adapted to the volume of work. Throughput times are reduced if means of transport are in the right place at the right time. The yard-spanning administration and control effort is reduced with high process stability.
Increasing automation makes processes less error-prone and better coordinated. This reveals further cost reduction potential.
You want to take the next step towards a smart yard?
The topic of hardware connections (scales, terminal, camera systems etc.) plays an important role in the creation of intelligent logistics systems, as does the integration of mobile devices. Therefore, a simple standardized integration capability of yard management systems is a basic component of yard control.
We recommend that you decide on a software solution first. For SAP customers, leogistics GmbH offers the leogistics d.s.c. In addition to the basic functions, you will find optimal options for mapping IoT scenarios and relying on smart processes. In the non-SAP area, we offer you myleo / dsc, a cloud-based logistics platform from which you can select modules individually or use them in any combination.
You would like to experience our solutions in detail? Contact us!
If you have any questions about this or other topics in the blog, please contact blog@leogistics.com.
André Käber
Jan-Philipp Horstmann
leogistics Yard Management & myleo / yard




