Warehouse Management (WM), Stock Room Management, embedded EWM or decentralized EWM - a colorful bouquet of possibilities
When customers consider an SAP S/4HANA implementation, they also need to think about a strategy regarding their warehouse management. But with the new S/4HANA world, the possibilities
Many customers today use the proven SAP WM module because it works easily and fully integrated with other logistics modules (MM/LES/PP). From a management of a simple high rack to the connection of a material flow computer – SAP WM makes it possible and runs reliably. In addition, the scanner RF technology, which has been used in many places for years, reliably supports mobile data capture.
SAP WM is soon to be phased out - decisions should be made
Even though SAP WM is a loyal companion for many customers, it should not be forgotten that the introduction of SAP EWM (Extended Warehouse Management) stopped the further development of SAP WM. Instead, SAP EWM is now the strategic product that SAP continues to promote today.
With the introduction of the S/4HANA world, SAP originally wanted to phase out the WM module by the end of 2025 and rely completely on EWM. However, it quickly became clear to everyone that a great many customers were running SAP WM and thus they had a stomach ache with a rapid changeover by 2025.
As a result, SAP accommodated customers and has now extended support for ERP ECC 6.0 until 2027 or 2030 (for a fee) on the one hand, so that customers have more time to make the switch. On the other hand, Stock Room Management has been established within the S/4HANA world.
Spoilt for choice: Warehouse Management (WM), Stock Room Management, embedded EWM or decentralized EWM?
Now companies are faced with the difficult decision of which path to take with an SAP S/4HANA implementation. The bouquet of options has grown significantly. The customer must now ask himself, “Which solution do I want to implement my S/4HANA with?” They can make the choice between Warehouse Management (WM), Stock Room Management, embedded EWM or decentralized EWM.
When we go into preliminary discussions with our clients, they often mention that they want to move away from SAP EWM. The complexity of SAP EWM is high and the employees should not be overstrained. In addition, many shy away from the supposedly high costs for the license. As soon as we ask deeper questions, it becomes clear that some do not even know what benefits the use of SAP EWM can provide compared to SAP WM.
Our tip: before making the switch, develop a clear picture of all the pros and cons of SAP WM and SAP EWM.
From my point of view it is advisable to arrange a half-day workshop with the customers, where a consultant presents the differences between SAP WM and SAP EWM and in the end even develops a new target picture. This is exactly where I would like to start in my blog and show the differences between SAP EWM and SAP WM with their advantages and disadvantages. My goal is to give a better impression of what it means to choose SAP EWM or SAP WM. In the end, there is no one true solution. Hybrid models are also possible. I recommend analyzing warehouse by warehouse and deciding on one path at a time.
In the following sections, I will specifically compare embedded EWM with WM. Although SAP strives for functional equality between an embedded EWM and a decentralized EWM, there are individual functions that exist in the embedded EWM that are not possible in a decentralized SAP EWM. This is solely due to the fact that the embedded EWM runs on the same instance as the S/4HANA in order to be able to use synergies.
SAP EWM versus SAP WM - all designations and organizational units
First of all, there are significant differences in the naming of organizational units, as well as various objects.
Basically, SAP EWM uses four-digit numbers for warehouse numbers, storage types and storage sections. For storage bins you can even use 18 digits instead of ten. The new feature of storage bins is that they are unique within the warehouse number and it is not possible to assign the same bin number twice.
Out of habit, SAP WM used to talk about plants and storage locations. In SAP EWM, we no longer speak of the plant, but of the party entitled to dispose , which represents a business partner. Storage locations are represented as an availability group.
| WM | embedded EWM |
|---|---|
| plant | party entiteled to dispose |
| storage location | avaibility group |
| stock type | stock type |
| supply-chain-unit |
comparison of the organizational units
New terminology in SAP EWM
The familiar terms “transfer order”, “transfer requirement” and “storage unit” are also no longer present in SAP EWM. Here we speak of “warehouse requests” and “warehouse tasks”. However, SAP EWM introduced the new object “warehouse order”. A warehouse order can have several warehouse tasks and thus forms the bracket for warehouse tasks. One or more warehouse tasks are assigned to the warehouse order as an item.
For palletizing and creating a storage unit in SAP WM, the quantities and the unit of measure are stored in the warehouse management view 2 and retrieved in the process. In SAP EWM, in the future the packing process will be supported via packing specifications and the known condition technique in SAP. This now makes the latter more flexible.
In addition, there is the organizational unit ”work center“, which is mapped via a storage type. This is used, for example, to map the packaging process.
For resource management, there is now the object ”Resource“, which maps an employee or a material handling equipment (e.g. forklift), so that, among other things, you can also manage the stocks on a resource. The resource is the prerequisite for using the RF applications.
| WM | embedded EWM |
|---|---|
| transport requisition | inbound delivery |
| transport order item | warehouse order |
| transport order | warehouse order |
| storage unit qtv | packing specification |
| - | work center |
| - | ressource |
| storage unit | handling unit |
Comparison of the objects
A closer look at the new system
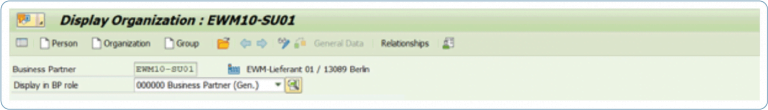
1. Business Partner
There are changes in both material master data and suppliers/customers. Basically, business partners are used on an S/4HANA system, so there is only one number for a partner. The distinction between suppliers or customers is made via so-called roles and is maintained centrally via the transaction “BP”.
2. Material master data
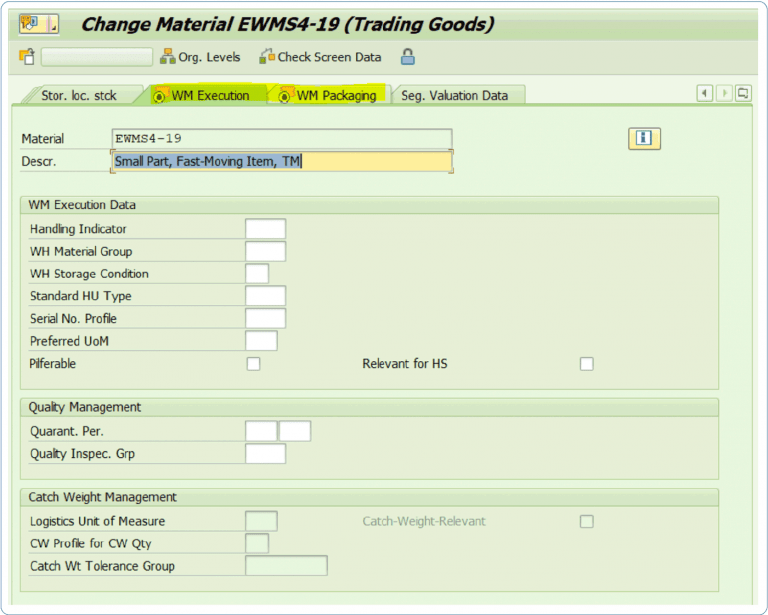
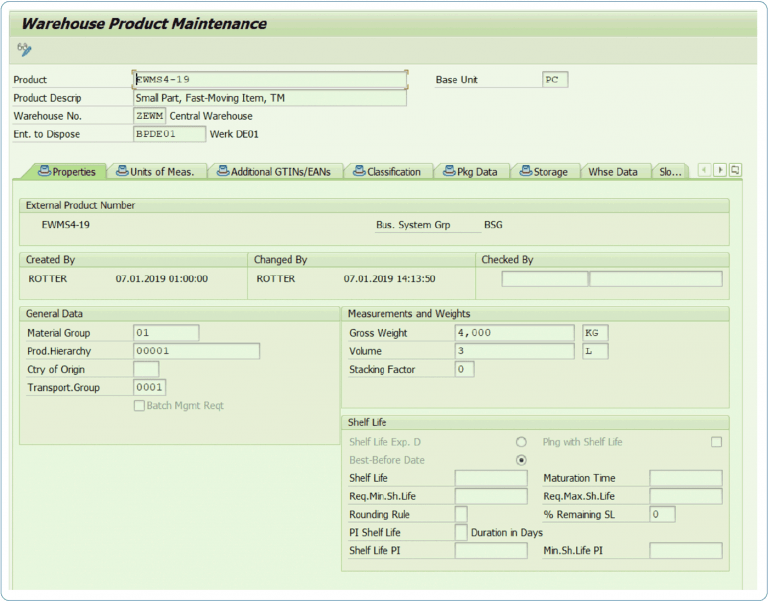
The main difference between SAP WM and SAP EWM is the material master data. Today, SAP WM is exclusively covered by transaction MM01 (Warehouse Management 1 and 2). In SAP EWM, it is possible to have a two-track approach: One option is to maintain certain data via transaction MM01 (WM Excecution/WM Packaging). The other option is to maintain the master data via the SAP EWM transaction /SCWM/MAT1 to SAP EWM.
The data from MM01 is also automatically transferred to SAP EWM after saving, so it is also visible in /SCWM/MAT1. However, if you want to define a putaway type indicator for the material, for example, the maintenance has to be done via SAP EWM. As soon as it becomes clear which fields need to be maintained, a concept should be developed that shows in which transaction which field needs to be maintained.
The exchange of master data between SAP ERP and SAP EWM also no longer takes place via the CIF (Core Interface) as usual. This has become obsolete with S/4HANA.
MM01:
/SCWM/MAT1:
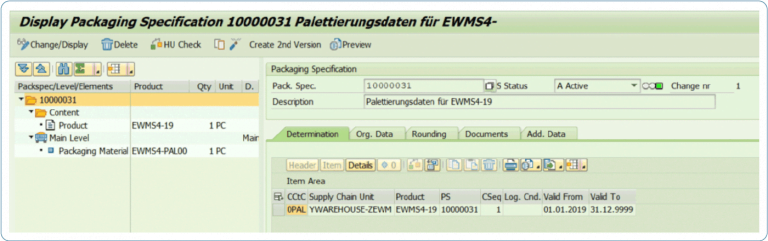
3. Packing specifications
Until now, palletizing data for storage units was maintained in the material master in SAP WM. With SAP EWM a new approach is taken. SAP uses the flexible condition technique to create handling units in SAP EWM. With the transaction /SCWM/PACKSPEC it is possible to store all necessary info, (HU type = storage unit type, weight, dimensions, quantity, packaging material) for the packaging process. The function is roughly comparable to the current packing logic for Handling Unit Management in the ERP system, where one uses the packing instructions or packing determination via transaction POF1 and POP1 for the packing process.
We are here for You!
If you are also thinking of making the switch, let us know. In our next article, we will take a closer look at how process flows and functions compare in SAP EWM versus SAP WM. We will support you in making your operational processes more efficient, transparent and cost-saving, thus improving your supply chains. Have we sparked your interest? Then please feel free to contact us!
If you have any questions about this or other topics in the blog, please contact blog@leogistics.com.
Daniel Rotter,
Senior Consultant SAP Logistics
BLOG &
NEWS
Latest news and blog posts from the world of intelligent supply chain management.




